Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025Warehouse managers need to understand the importance of measuring warehouse performance. It is crucial to measure performance because it helps companies keep track of trends, assess efficiency, and identify any problems that may arise.
When it comes to measuring warehouse performance, there are different approaches you can take. You can begin with the traditional method or utilize specific metrics or Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) tailored for warehouses. In this section, we will describe alternative methods for measuring warehouse performance.
Measuring warehouse performance is essential for companies to understand how well their warehouses operate. It helps them in a few key ways:
When warehouse managers can identify issues, evaluating and fixing them becomes more manageable. There are many ways to measure warehouse performance, all aimed at objectively assessing and evaluating warehouse activities.
Read more: Understanding Warehouses: Definition and its Importance
According to Ackerman (2003), measuring warehouse performance involves focusing on four key areas:
Performance management effectively manages various aspects of a company’s operations and economic performance. According to Slack et al. (2001), high-performance procedures can be described as follows:
To effectively measure performance, it’s essential to monitor how well you meet the criteria that matter to your customers and how well you manage costs.
The figure below shows that different industries have different ideas about what matters most in measuring performance. It illustrates the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that retailers find essential and the ones that their third-party logistics service providers prioritize.
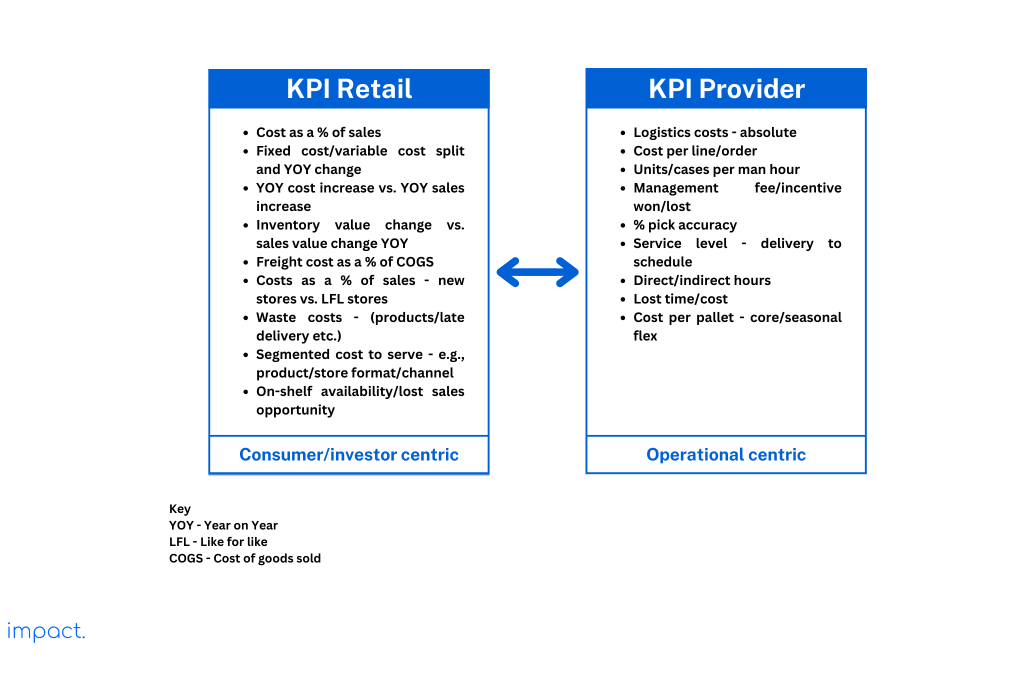
To effectively measure performance management, it is crucial to record and analyze the time it takes to complete various tasks in the warehouse. Consider the following factors when measuring these activities:
There are several ways to measure warehouse performance management, and each method has its benefits. Different companies have different priorities, customers, and ways of doing things. To choose the best approach, you should follow these steps:
The first step in creating a sound performance measurement system is understanding the company’s vision and how your department can help achieve its goals. Sometimes, department heads develop performance measures they find comfortable and easy to achieve. Still, these measures don’t match the company’s vision and don’t interest senior managers.
It’s essential to follow the SMART approach to achieve success. Your actions should meet the following criteria:
Moseley (2004) and Vitasek (2004) suggest the following tips for introducing KPIs:
Companies can choose from six different methods to measure warehouse management performance. Let’s take a look at each type of measurement method:
In today’s warehouses, we use several traditional ways to measure productivity. These measures fall into four main types:
| Hours worked: (Hours worked × 100) ÷ hours worked available |
| Warehouse area utilization: (Used space × 100) ÷ available space |
| MHE utilization: (used MHE hours × 100) ÷ available MHE hours |
In financial terms, a cost measure represents a percentage of sales and the cost incurred per order shipped. To calculate this measure, follow these steps:
| Percentage cost of sales: (Total warehousing costs × 100) ÷ total sales revenue |
| Order costs shipped: Total warehouse cost ÷ total number of orders shipped |
| Picked units per hour: Units picked ÷ total available hours |
| Delivery accuracy : Unit selected ÷ total hours available |
| Timely delivery: Orders shipped according to customer requests ÷ total orders received |
OTIF (on time and in full) is one of the most commonly used metrics in the UK today. It combines with the perfect order metric, the most popular measure of customer service. To meet the OTIF standard, we must deliver items on time, without any damage, and ensure they have the correct documentation and labeling. Moreover, accurate invoicing is crucial.
Let’s break down the calculation for the perfect sort percentage. We measure four metrics individually and then multiply them:
To find the perfect order metric, we multiply these percentages: 97% × 98.5% × 99.5% × 98% = 93.2%.Now, let’s focus on the OTIF (On-Time-In-Full) measurement. It considers two metrics: on-time delivery and delivery in full. The yield for OTIF is calculated as 97% × 98.5% = 95.5%.
Additionally, our latest warehouse measurements include inventory evaluations. When assessing inventory, we should measure the following aspects:
To calculate the stock turnover, divide the current stock level by the total annual sales and multiply the result by 365. You can calculate this using the actual number of units in stock or the stock value. This calculation helps us determine how many days’ worth of stock we have.
For example, let’s look at the table below. It shows that product code 99172100 has been in stock at the warehouse for two and a half years. On the other hand, product code 90152100 has only been in store for five days.
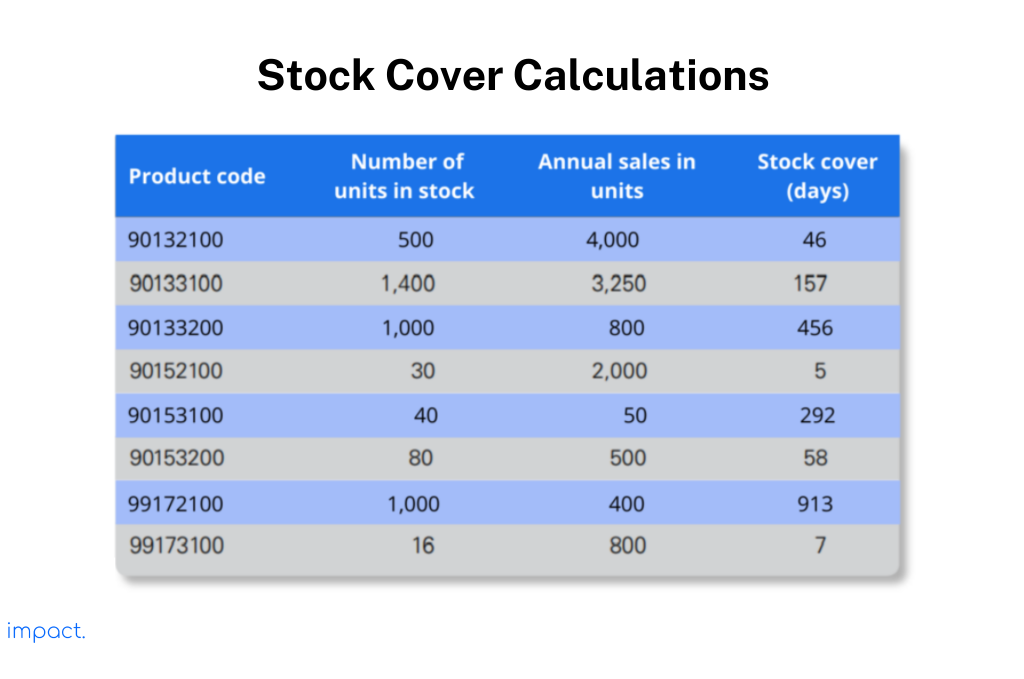
To calculate stock turnover, divide the total units sold by the average number of units available. For example, product 90132100 sold eight units in the past, which is considered reasonable. However, product code 99172100 only had a stock turnover of 0.4, meaning the stock turnover was less than once yearly.
This calculation helps determine stock ordering policies and decide whether to return stock to producers, discard it, or launch sales campaigns.
Inventory measurement includes assessing stock accuracy, which ensures efficient order fulfillment. Whether you count stock once a year, twice a year, or daily using cyclical or perpetual inventory counting methods, maintaining accurate stock levels is crucial. The more precise your stock records are, the better your chances of fulfilling orders correctly and increasing overall efficiency.
To measure stock accuracy, follow these steps:
To determine the extent of damage in the warehouse, you can measure it in two ways. First, divide the damaged goods by the total number of items processed through the warehouse. Second, assess the monetary value of the damage.
| Percentage of damaged items = items found to be damaged ÷ items shipped per month |
The measurement forms mentioned earlier are known as hard measures. They are relatively easy to measure, concrete, and straightforward. In contrast, soft measures refer to intangible qualities.
For instance, consider customer satisfaction with prompt delivery as a soft measure. Soft measures effectively capture perceived changes and provide a more comprehensive understanding of success than narrow-focused strict measures.
Although it can be challenging, soft measurement can be defined and measured. For example, we can use a survey with a rating scale from 1 to 10 to assess user satisfaction. This survey can be repeated at appropriate intervals to track perceived changes in service.
Research conducted by Landrum et al. (2009) highlights reliability and responsiveness as the most critical factors for service quality. Reliability factors include:
The integrated performance model blends actual performance data and customer perceptions. We gather data from performance reports and send questionnaires to customers regularly.
We assign ratings based on survey results and actual performance, which produce scores. We use red, yellow, and green models to highlight poorly performing areas. Red areas require attention.
When measuring performance, make sure your actions match customer requirements and expectations. For example, delivering 100 percent of available warehouse items doesn’t always mean fulfilling the exact customer order quantity.
Benchmarking is when a company compares its performance with other companies or operations. The goal is to discover what successful companies do to achieve high performance.
Companies use benchmarking to:
When benchmarking, it’s important to collaborate, keep things confidential, provide value, be flexible, honest, open, and maintain a good reputation. One way to keep things hidden and anonymous is to involve outside parties like benchmarking groups, consultants, or universities.
Kaplan and Norton (1996) created the balanced scorecard, which tracks performance. It assesses aspects like finance, customer satisfaction, internal processes, staff development, and innovation.
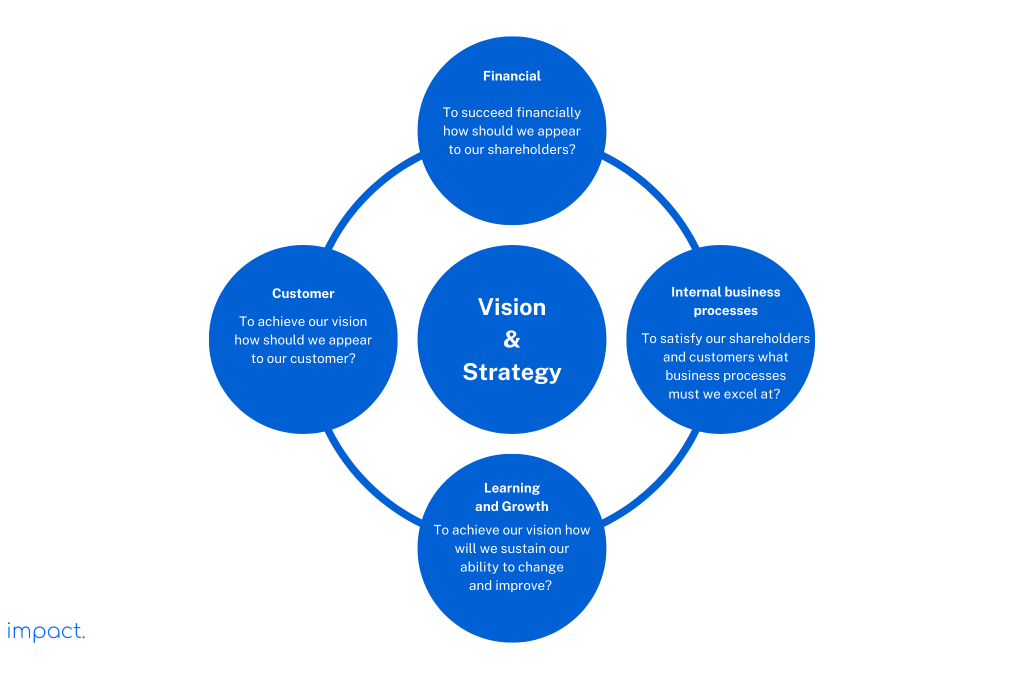
We will set goals and targets for each measure and measure them against actual performance. By implementing a balanced scorecard approach, we aim to improve processes, motivate teams, increase customer satisfaction, and enhance communication.
Read more: Warehouse Manager: Roles and 10 Challenges to Overcome
To achieve efficient operations, measuring performance effectively by following SMART steps that align with the company’s strategic vision is essential.
It’s worth noting that traditional KPIs report the status of an operation or process at a specific time. While they help compare performance over time, adjusting targets and actions is crucial as the environment changes quickly.
There are many performance measures related to warehouse operations. However, it’s best to measure only the areas that matter to your customers and your company.
Richard G. 2011. Warehouse Management. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
See how our ERP provides better value.
Speak with our consultant to explore how we can improve your accounting, processes, and people.
