Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025Company culture starts with the people in it. Human Resources (HR) is crucial in lean manufacturing as the heart and soul. At Toyota, HR is at the center, providing the most essential input for the company: its workers.
HR is also vital in supporting a thriving lean culture within a company. Let’s now explore lean culture in more detail, including its definition, how it came to be, and the factors contributing to it.
Organizational culture includes how team members experience their daily work and what they do. On the other hand, lean culture puts customers first and always looks for ways to get better.
In a lean culture, team members treat each other equally and respectfully. This interaction creates a collaborative environment where there’s no competition between workers.
Four pillars form the foundation of lean culture. These pillars are:
Read more: Lean Manufacturing: Definition & 3 Benefits
We need everyone to spot and remove waste to create a lean culture. It means working together and sometimes changing how we think. However, more importantly, it’s about agreeing on what we consider wasteful or valuable. Here are two things to remember when building a lean culture:
Leadership in a company has a significant impact on things. Managers must take charge, start conversations, and show good examples. In a lean culture, the manager’s job is to handle the work, not the people. By managing the workflow, we can create a team where everyone works together to achieve the goals.
The cultural framework is essential for both new employees and existing team members, who sometimes wonder how they should act. It provides guidelines and expectations for everyone in the organization. When companies create a framework that lists standards and desired behaviors, it brings clarity and agreement on how to do things. The framework helps everyone understand their expectations.
Six supporters drive the formation of a lean culture and are actively present in companies that embrace lean principles. Here is a breakdown of each type:
PDCA is a simple four-step method that helps avoid mistakes and improve business processes. It’s an essential activity for managers. Here are the key points:
For effective learning of PDCA, practicing it under the guidance of an experienced mentor is recommended. The HR department should also consider how to support mentoring in our organization.
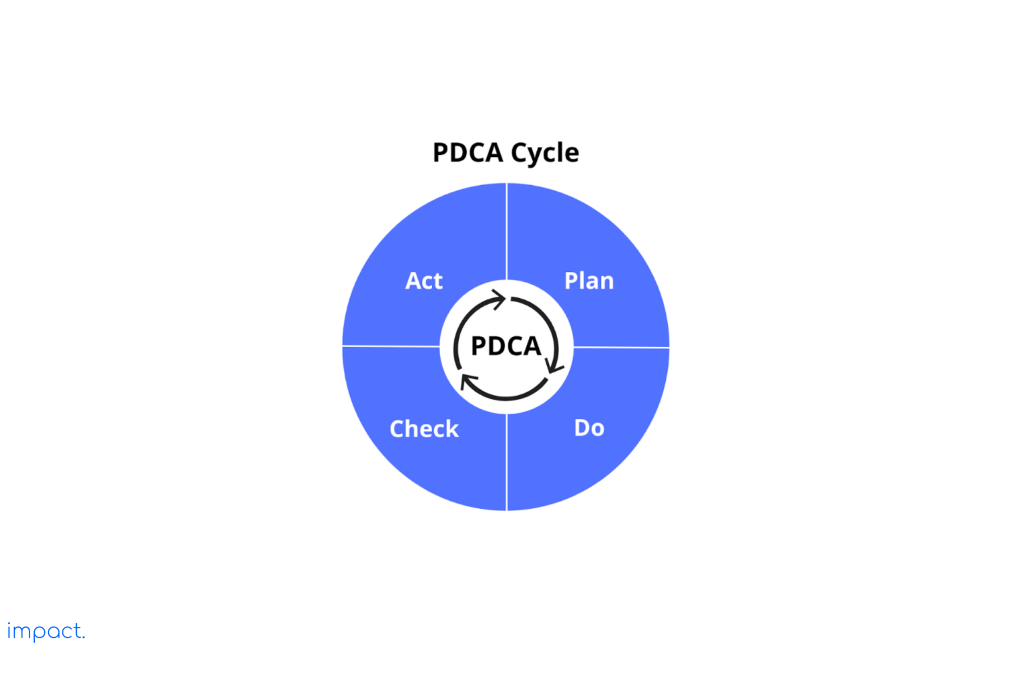
The company must establish its direction and goals to create a plan. It should then provide different ways to achieve those goals. A good plan should include the following:
The critical planning results are Gantt charts, backup plans, and control panels or dashboards.
Do has its own PDCA cycle, emphasizing the importance of trying things out before fully implementing them. Conducting successful trials helps us strengthen and validate our plans.
PDCA requires assessing team members’ abilities objectively to avoid any skill gaps. Human Resources must clearly understand what “capability” means to evaluate the current situation and take appropriate actions accurately.
Companies must make several decisions when it comes to checking and confirming information. They need to determine whom to check with, what to check when to check, how often to check, and how to conduct the checks. This process enables companies to gain a comprehensive understanding of all the events taking place within the company.
The “go-see” approach is crucial because it accurately accounts for what occurred and eliminates the risk of errors by merely checking
Acting involves thoughtful consideration of a situation and subsequent action. It encompasses two key aspects:
Experience has taught us the importance of being prepared. We use temporary measures to address minor issues and permanent solutions to the root causes. Companies should also stay focused on taking action while considering future gaps in skills and training needs.
The previous chapter discussed how standards are crucial in Lean manufacturing systems. They are a powerful tool for continuously finding better ways to do things.
Companies have the freedom to create their standards. Rather than constantly reprinting documents with changes, it is more efficient to maintain a record of the changes and their corresponding dates. It’s essential for the standards to clearly state what is considered normal and what falls outside of that.
Let’s take a messy workplace without standards as an example. It’s difficult to spot problems like equipment leaks in such a place. On the other hand, if the workplace is clean and has clear standards, any abnormal conditions can be quickly identified and fixed.
Visual management is a technique that utilizes images and minimal text to achieve the visual management triangle. The accompanying image demonstrates this concept.
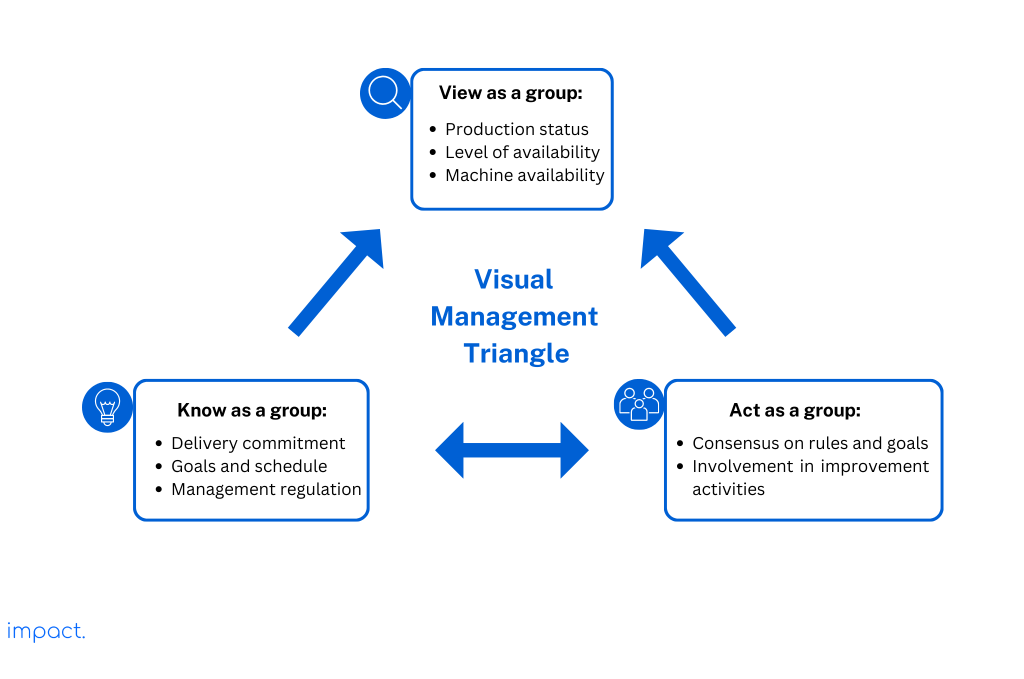
Visual management is a way to show and explain how the company’s work system operates. Toyota treats visual management like a play, organizing events on the shop floor to make problems easy to see. Here are some of the events they do:
Working together as a team is crucial for achieving goals. Here are some ways to improve teamwork in a lean culture:
Read more: Employee Involvement: Significance & 3 Supporting Factors
Lean manufacturing is full of unique and exciting paradoxes. Paradoxes are things that go against common beliefs. Here are some examples of the paradoxes in lean manufacturing:
PDCA, standardization, and visual management build a solid lean culture. This culture promotes Kaizen, a continuous improvement process that aims to reduce waste in manufacturing through minor ongoing improvements.
Without Kaizen, a Lean manager may work 90 hours per week. However, with a culture of intensity, managers can easily spot areas for improvement and value, which helps reduce their working hours.
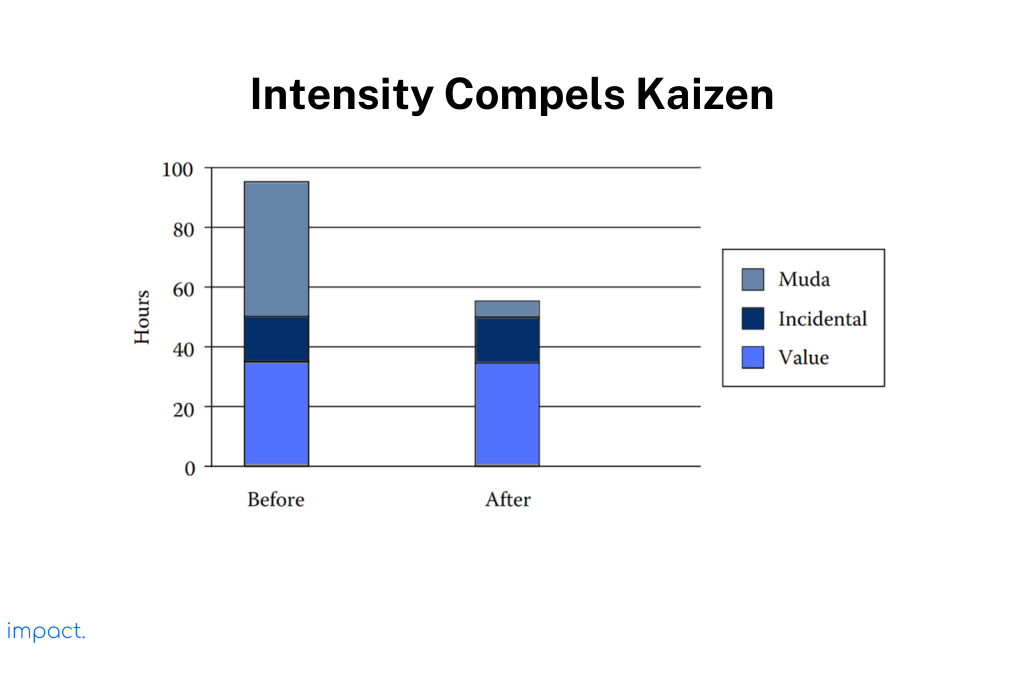
Managers must stay close to their teams and provide support when needed while keeping the intensity high. As the company eliminates inefficiencies over time, work becomes more efficient.
A lean culture is all about focusing on customers and constantly improving. Six critical factors support a lean culture: PDCA, standardization, visual management, teamwork, intensity, and paradox.
Everyone in the company needs to participate actively to create a lean culture. Managing human resources within the company has become simpler using HCM Impact. It’s a tool that automates HR management processes.
Dennis, P. (2017). Lean production simplified: a plain-language guide to the world’s most powerful production system. Crc press.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
See how our ERP provides better value.
Speak with our consultant to explore how we can improve your accounting, processes, and people.
