Kanban: Definition, 6 Rules, and its Benefits
Kanban is a crucial part of the Just in Time (JIT) system, which we discussed…
Sean Thobias
May 17, 2025In the previous chapter, we discussed the “Customer Development Manifesto.” It contains 14 critical ideas that startups use in the Customer Development Process. These ideas have been beneficial to many entrepreneurs in building successful businesses. Now, let’s shift our focus to another crucial aspect of entrepreneurship: creating a successful web startup.
In today’s digital world, web startups are becoming increasingly important. But what exactly is a web startup, and how can you start one successfully?
This article isn’t just about explaining a web startup; it’s a practical guide to help you turn your ideas into a real business. We’ve taken many insights from “The Startup Owner’s Manual” by Steve Blank and Bob Dorf to provide you with tailored advice on how to take concrete steps toward making your dreams a reality.
Keep reading this article to learn the ten essential steps to guide you through this exciting business journey. Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or just starting your first startup adventure, this chapter will help you understand and master the art of building a web startup.
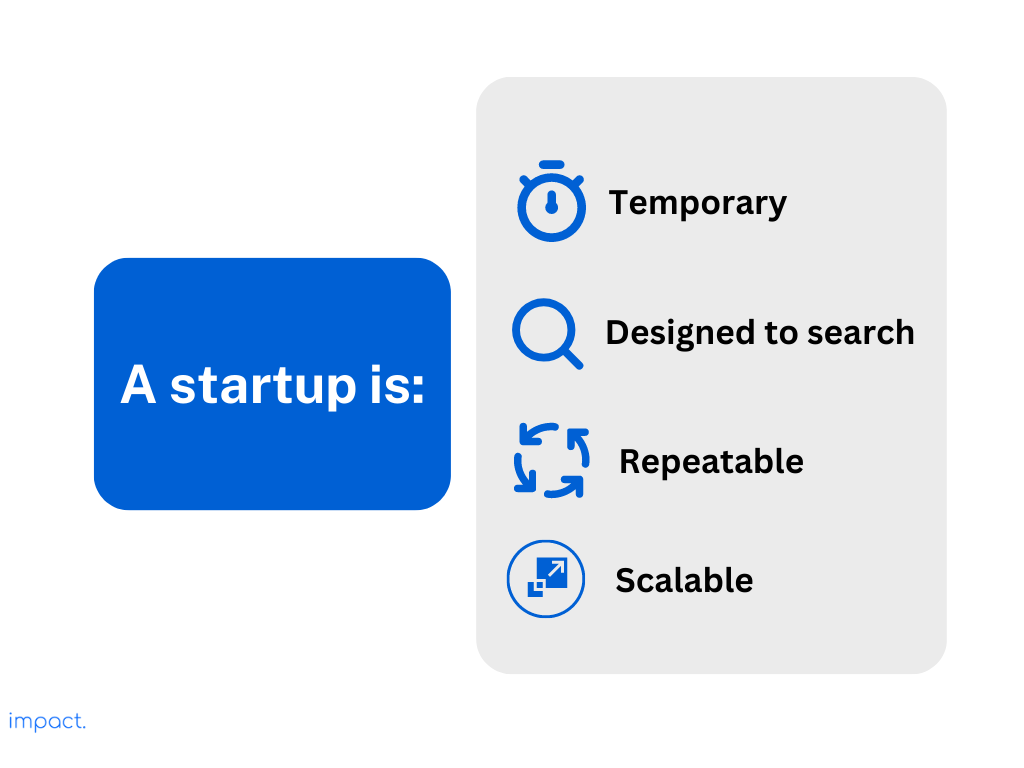
In our first chapter, we looked at Steve Blank’s definition of a startup. He describes a startup as a temporary organization trying to find a business idea with a repeatable and scalable business model.
Now, let’s focus on web startups. These are a special kind of startup that mainly works online. They’re different from regular startups that might sell physical products. Web startups offer digital services or products. They use the internet to connect with customers, provide services, and generate revenue.
Here’s how web startups differ from regular startups:
Read more: Startup Essentials: Key Definition and 9 Mistakes to Avoid
Many companies are moving their operations online, and some are even starting their businesses online. This shift isn’t always a choice; often, it’s a necessity.
As we all know, the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020 significantly changed how we conduct business. Many companies were caught off guard by the new restrictions and shutdowns. However, many businesses could adjust and persevere — by going online.
Financial experts at Gartner, Inc. found that Chinese companies that did best during the pandemic were those that teamed up with trusted online service partners and used automation in their business plans.
In addition to changing habits, customers are also the driving force of this shift. Today, more people than ever are turning to the internet for their shopping needs.
By 2025, e-commerce businesses will generate a staggering $7.4 trillion in sales. Even though you might think big online stores rule everything, there’s still room for online shops focusing on unique interests and making customers happy.
Starting a web startup can be an exciting but challenging journey. To guide you through this process, we’ll follow the proven steps outlined by Steve Blank. These ten steps will help you set up your web startup from scratch and increase your chances of success.
First, ensure your team is ready, and you’re on the right track with your startup. Start by understanding the Customer Development Model, which helps you know your customers better.
Create a WordPress Blog to document everything you learn about your customers. This blog will be like your startup’s diary, helping your team stay on the same page and keep track of your progress.
To chat with your team, use Skype and Zoom. They’re great for team talks and meetings, especially if your team members are in different places. Good communication is critical to making your startup work, and these tools will help you chat, share ideas, and make decisions together.
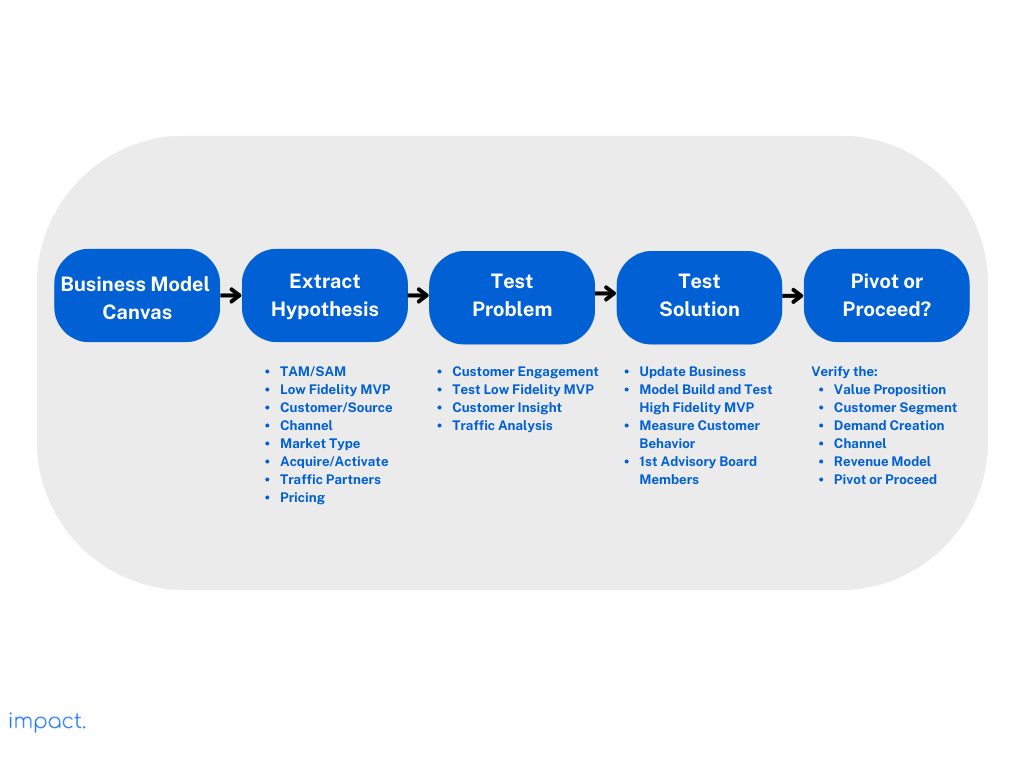
The next step in creating a web-based startup is to craft your company hypothesis. This step involves laying the foundation for your business by defining your strategy, understanding your market, and outlining your initial product offerings. Here are key points to consider during this phase:
Start by creating a comprehensive Business Model Canvas that outlines your business’s core components. This model should include hypotheses about your value proposition, customer segments, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, essential resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. These ideas will be like the building blocks for your startup’s strategy and help you choose what to do next.
Identify the key features that are essential for your MVP. Focus on the minimum set of functionalities that will allow you to test your hypotheses and gather valuable user feedback. These features should address your target audience’s most pressing needs and pain points while keeping development costs and timeframes in check.
Use tools like Google Trends, Google Insights, and Facebook ads to see if enough people are interested in your business idea. Look for signs that the market is growing. Also, look at what other companies are doing in the same space.
Use Crunchbase and other relevant tools to research your competitors. Understand their strengths, weaknesses, market positioning, and customer base. This analysis will help you identify gaps in the market that your startup can exploit and determine how your product or service can stand out.
Calculate the Total Available Market by estimating the total number of potential customers in your chosen market segment. Consider age, location, and other factors that define your target customers. Also, consider how much each customer might be worth to your business over time.
Determine the market type your startup is entering, which could be one of the following:
Selecting the right market type is crucial as it influences your go-to-market strategy, competitive positioning, and marketing approach.
Read also: Customer Development Process: 4-Step Framework for Startups
Next, it’s time to formulate a concise and easy-to-understand description of your company. This statement should explain why your business exists in an easy-to-understand way. You can use a format like “We help X do Y by doing Z” to make it straightforward.
After you’ve written this statement, ask a few people (even if they’re not your exact customers) if they understand your business. If they’re confused, explain your startup in more detail and ask them for feedback.
Others can give you helpful ideas and suggestions to improve your value proposition, making it more understandable and appealing. Their fresh perspective can help you create a statement that connects with your target audience, sparks their interest, and makes them want to learn more about your web startup. Remember that a well-defined value proposition is the cornerstone of a successful business.
The next step for your web startup is setting up the website logistics, which is crucial for your online presence. Here’s what you need to do:
However, you can set up a web host if you know how to code.
Setting up the logistics of your website is just the beginning. Creating a simple website is part of the next step. This website should tell people what your product or service is and what they can benefit from. It should encourage them to take action, like learning more, filling out a survey, or pre-ordering.
For non-tech experts:
For coders:
After creating the website for your startup, your task is to get people to visit your website. After all, your brilliant idea and well-designed Minimal Viable Product (MVP) won’t mean much if no one knows or uses it. You need to employ a multifaceted approach to draw potential users to your site and begin validating your customer segment and value proposition.
In short, to get customers to your web startup, you need a mix of paid ads, SEO, networking, email marketing, and surveys. These methods will bring visitors to your site, and their feedback will help you improve your product and attract more customers.
Read more: Social Media Marketing: A Guide & 3 Strategies for Success
The next step for your web startup is to connect your user interface (UI) to a web application framework. First, pick the proper framework based on your needs and your team’s skills. Some popular options include Node.js, Ruby on Rails, and Django.
After selecting a framework, it’s time to integrate it with your user interface (UI) by transforming your design into functional code. This connection is crucial for making your startup operational. Begin building the essential components of your startup, such as user registration, backend logic, and databases. It’s vital to ensure that your application functions well and can accommodate a large user base.
Don’t forget to test and fix any problems you find. User feedback helps make your app better. Also, use analytics to understand how people use your app. This information enables you to make more improvements.
The next stage of creating a web-based business is to test the identified “problem” with the data you get from customers. This phase is about deeply understanding your target audience, their needs, and how your product or service can address those needs effectively. Here are some key points to consider during this step:
To understand how people use your website, you need web analytics tools. Google Analytics is a good start. It tells you how many people visit your site, how long they stay, and where they come from. This info helps you know if people like your site and which marketing works best. Later, when your startup grows, you can check out more advanced analytics tools for better insights and options.
Set up accounts on user feedback websites. These sites let users share their thoughts, problems, and ideas directly. This approach shows them you care about making their experience better.
When you ask users specific questions, you get better feedback. For example, ask, “Is there something stopping you from signing up?” or “What more info would make you like this solution?” These questions make users share their issues and hopes so you can make your product even better.
Ask users for their email addresses; it lets you communicate with them personally. You can check back with users who shared feedback to learn more, have chats with them, or even give them early access to new stuff to say thanks. Having their email helps you stay in touch and understand them better.
It’s time to test your startup idea by creating a polished website. Here’s what you need to do:
The last step in launching your online startup is receiving payment. Here’s how you can do it:
Picking the right billing provider is crucial. Ensure they fit your business model, have reasonable pricing, and offer good customer support. Also, set up your billing processes properly, like deciding on prices, managing discounts, and handling any issues that might come up during transactions.
We’ve covered some important information about web startups in this article. These startups differ from regular ones because they offer digital products or services and use the internet to connect with customers exclusively. They can reach people worldwide, cost less, and scale faster.
We have provided you with a ten-step roadmap based on Steve Blank’s advice to help you launch your web startup. These steps will guide you in setting up your business from scratch and seeking funding at the right time.
The upcoming chapter will delve into the business model canvas – a crucial tool for developing your startup. We will examine all of its nine components.
Blank, Steve, and Bob Dorf. The Startup Owner’s Manual: The Step-By-Step Guide for Building a Great Company. 2020.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
See how our ERP provides better value.
Speak with our consultant to explore how we can improve your accounting, processes, and people.
