Business Model Canvas: 9 Components to Map Startup Success
The last chapter explored the essential steps of creating a web startup, using steps from…
Sean Thobias
September 25, 2024Our retail guide’s last chapter explored ways to boost your store’s success through innovative finance, operations, and customer relations practices. As you manage your store, pay close attention to critical metrics and KPIs for a clearer picture of performance.
These retail metrics include sales, inventory, and customer data. Discover why these metrics are crucial, which ones to focus on, and get practical tips to enhance their effectiveness.
Measuring metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for evaluating individual and team performance in your business. This assessment guides performance reviews, goal setting, and improvement efforts.
Monitoring metrics and KPIs in retail is vital to assess overall business performance and alignment with strategic goals. The practice helps identify successes and areas for improvement.
Retail business owners, it’s vital to base your decisions on data for effective planning and execution. Metrics and KPIs offer valuable insights, showing what works well and pointing out areas that need improvement.
Use metrics and KPIs to optimize resource allocation. Identify high-impact areas so you can deploy resources effectively. It ensures your time, manpower, and financial investments go where they’ll contribute the most to your business success.
Keeping a close watch on significant numbers is essential for retail business owners. Check your cash flow and liquidity ratios regularly. These indicators can give you an early heads-up about economic ups and downs.
Keep an eye on your supply chain metrics, too. These metrics help you spot weaknesses, diversify suppliers, and be ready with backup plans. Taking these steps upfront lessens the hit if there are any bumps in the road for your business.
Boost your employees’ performance using metrics and KPIs to measure their satisfaction and productivity. These metrics serve as a straightforward scorecard, giving your employees a clear picture of their performance.
Equip your team with essential metrics to help them establish and achieve meaningful goals. This accountability fosters a culture of responsibility and continuous improvement in your retail business.
Conversion rate is a must-watch metric for retail, whether online or in-store. It shows the percentage of visitors who purchase, giving you more insight than just counting transactions.
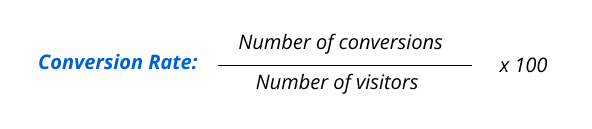
A high conversion rate means many visitors become customers, pointing to successful marketing and retail sales tactics. Keep an eye on this metric to spot where you can enhance the customer experience, like improving product displays, making your website more user-friendly, or smoothing out the checkout process.
Foot traffic means the number of people entering your store. You can track it using electronic counting systems or manually counting during peak hours.
Analyzing foot traffic alongside metrics like the conversion rate is crucial, as it helps you gauge how well your store turns visitors into customers. Also, comparing foot traffic across various periods unveils seasonal patterns and reveals the impact of marketing efforts.
Sales per square foot tells you how well you use your store space to make money. It’s a measure of how productive your layout, where you put products, and your overall use of space is in bringing in retail sales.

A high sales per square foot means your store setup is good, and customers enjoy shopping there. Check if all your stores or departments are doing well. If this number continues, your retail strategies work, and you use your space effectively.
ATV is the average amount a customer spends in one transaction. It’s critical for grasping customer buying habits and how well sales strategies work.
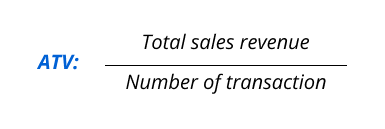
Increase your retail earnings by cross selling or having discounts on larger purchases to boost the average transaction value (ATV). Monitor trends and customer groups to make targeted improvements for maximum profitability.
Customer Retention Rate measures the percentage of customers a business retains over a specific period. It provides insights into customer satisfaction, loyalty, and the effectiveness of efforts to keep existing customers.

A rising CRR signals satisfied customers; if it drops, address product quality or customer service. Strive to balance acquiring new customers and retaining existing ones to ensure sustained retail success.
Gross profit margin is the percentage of money you make from selling your products after accounting for how much it costs to make or buy them.
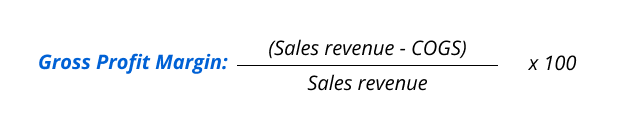
Aim for a higher gross profit margin because you manage costs well and effectively pricing your products. Keep an eye on this number to catch any issues with costs or pricing that might affect your overall profit.
Year-over-year (YoY) growth is a way to measure the percentage change in a specific business metric from this year compared to the previous year. This comparison provides a solid understanding of your business’s performance trends and helps evaluate how well your strategies work.

Analyze year-over-year (YoY) growth across sales, revenue, and customer acquisition for a comprehensive view. Positive YoY growth is encouraging, but understanding the reasons is crucial, while negative growth prompts a thorough examination of strategies and operations for improvement.
Inventory turnover shows how fast a business sells and restocks its products, telling you how well you manage inventory and if there’s demand for your goods.
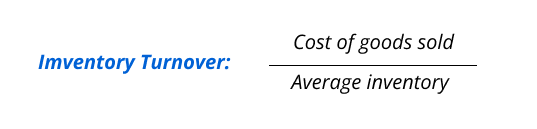
A higher turnover is good, meaning products are selling fast. Yet, if it’s very high, you might be running out of stock, and if it’s low, you could have too much stock or slow-selling items. Keep an eye on this to balance your inventory right.
The sell-through rate is a tool that helps retail business owners understand how efficiently they sell the products they have in stock. It’s calculated by dividing the units sold by the initial inventory quantity, providing a percentage that indicates the rate at which inventory turns into sales.
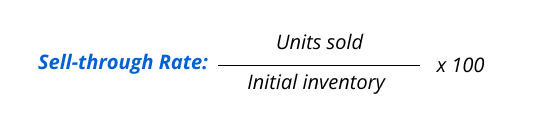
For retail businesses, a reasonable sell-through rate means products are selling fast, but be cautious of an excessively high rate that could lead to stockouts or a low rate indicating overstock. Regularly track this metric to fine-tune inventory strategies, ensuring optimal retail sales without excess or shortages.
The stockout rate is how often a retailer faces inventory shortages or runs out of a specific product, directly influencing customer satisfaction and potential retail sales.
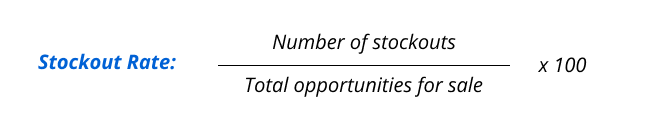
A low stockout rate in retail signals effective inventory management, preventing lost sales and maintaining customer satisfaction. Reviewing stockout data is crucial for optimizing inventory levels and strategically adjusting procurement or supply chain processes.
Shrinkage is the difference between the recorded and actual stock on hand, usually expressed as a percentage. It includes losses from theft, errors, and other unaccounted factors.

Excessive shrinkage can negatively impact retail profits, making it vital to monitor trends and address areas for improvement, such as security measures, inventory management, and employee training. Retailers must thoroughly investigate and address the root causes of shrinkage to minimize financial losses effectively.
GMROI is a key metric that helps you assess how profitable your inventory is by looking at the relationship between the gross margin and the average inventory investment.
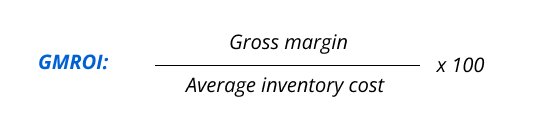
A higher GMROI indicates a superior return on inventory investment. Optimize profitability by balancing high gross margins, swift inventory turnover, and regularly adjusting product assortments and pricing strategies.
Choose metrics and KPIs that directly relate to your business objectives. It’s better to focus on several key indicators that provide actionable insights rather than measuring everything.
When assessing metrics for your retail business, focus on what truly helps you improve. Get rid of metrics that don’t contribute to your goals, concentrate on the ones that do, and skip unnecessary measurements to save time and resources.
Setting clear targets for your KPIs is crucial to measure your retail business’s performance effectively. Know your business goals and avoid setting too ambitious or unattainable targets.
When setting targets, consider realistic values that make sense for your specific retail context and look at industry benchmarks for guidance. Doing this will ensure your goals are practical and achievable, preventing frustration or setbacks caused by setting too high or unrealistic targets.
Once you’ve selected your metrics and KPIs, transform them into actionable insights instead of just numbers. Opt for visually engaging formats when presenting data, as 65% of the population learns better through visuals.
Streamline comprehension for stakeholders by incorporating dashboards and visualizations. Take advantage of tools that offer diverse dashboard options for a centralized presentation of your KPIs and metrics.
For retail business owners, integrating real-time monitoring is a game-changer. It gives you instant insights into crucial metrics like sales and operations, making it easier to make timely decisions and tackle issues as they arise.
Utilize ERP software to streamline real-time monitoring by consolidating data, ensuring accuracy, and facilitating informed decision-making for overall business improvement.
Ensure your retail metrics and KPIs stay current with your business goals and challenges. It sharpens your monitoring system, allowing for swift adjustments in response to market shifts.
Updating your metrics isn’t a mere formality — it’s a practical step to enhance your retail business’s agility. By fine-tuning your metrics based on real-time insights, you can proactively address issues and keep your store agile, ready to seize emerging opportunities.
Running a successful retail business requires careful attention to metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). Yet, manual tracking can be cumbersome and challenging due to the real-time nature and many variables.
For a more efficient approach, consider investing in an ERP system to streamline your operations. In the next chapter of our guide, we’ll delve into the various types of software and technology essential for retail businesses, highlighting their significance and providing insights on what to consider when purchasing.
Ramsey, D., & Ramsey, J. (2010). The Everything Guide to starting and running a retail store: All you need to get started and succeed in your own retail adventure. Adams Media.
Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.
75% of digital transformation projects fail. Take the right first step by choosing a reliable long-term partner.
